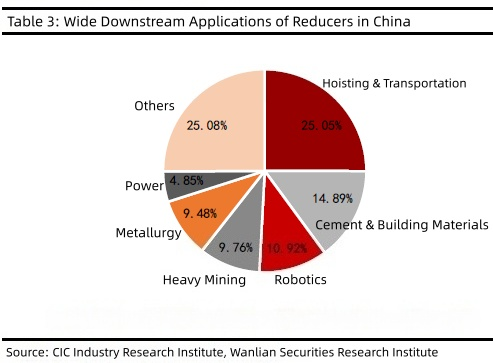
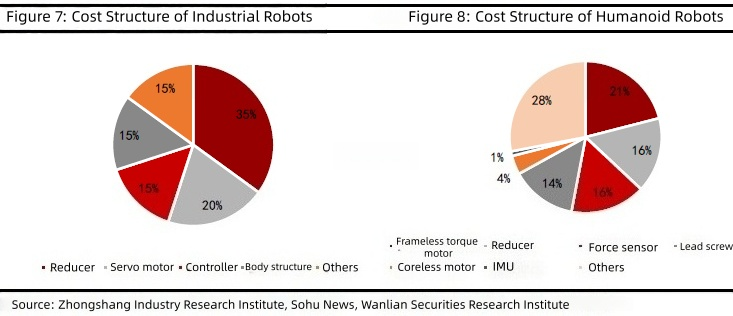
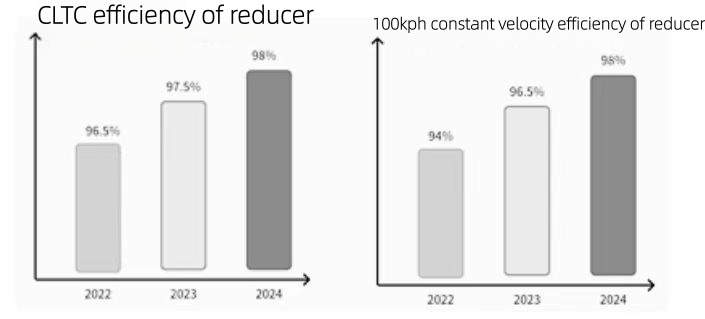
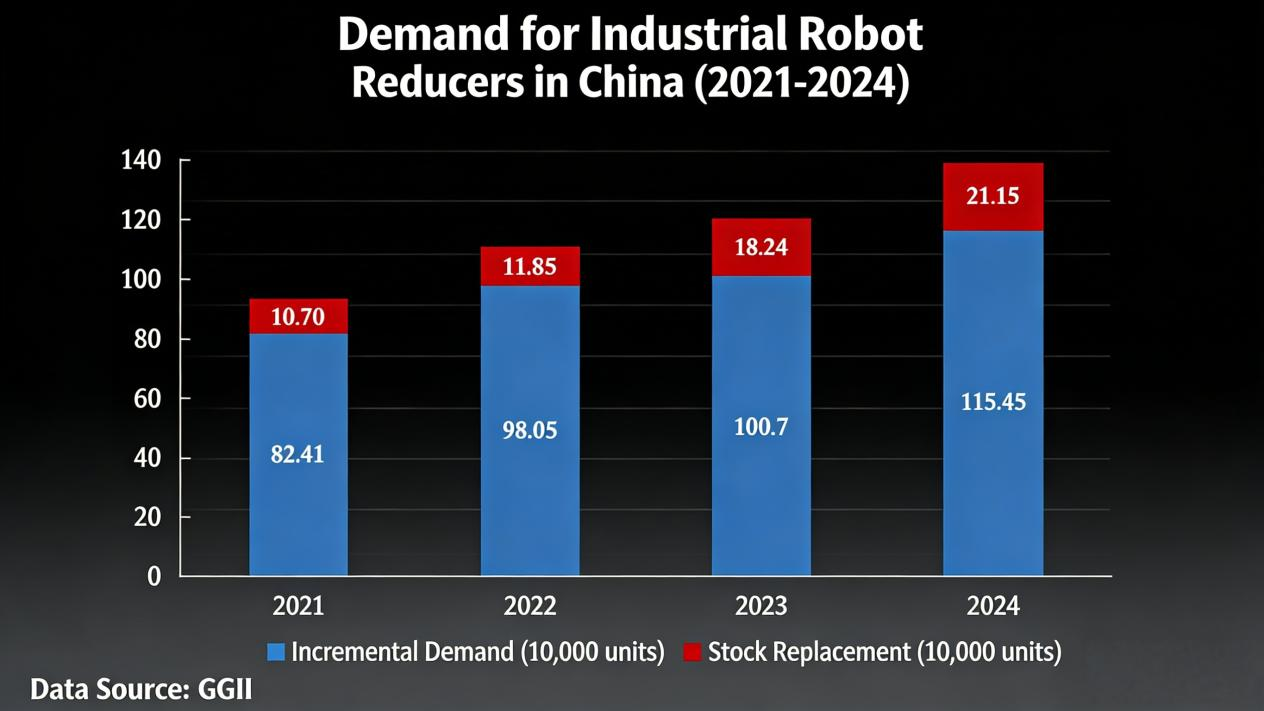
Os chips de GaN (nitreto de gálio), com suas principais vantagens de baixa perda e alta densidade de potência, superaram as limitações dos dispositivos tradicionais baseados em silício, emergindo como a principal direção de desenvolvimento para acionamentos de motores de média e baixa tensão. As principais vantagens dos chips de GaN incluem: Baixa perda de comutação: Característica de recuperação reversa zero, sem corrente de cauda, baixa perda de comutação do capacitor, perda de sobreposição tensão-corrente otimizada, reduzindo significativamente a perda total do sistema. Adaptabilidade a altas frequências: Suporta frequências PWM mais altas (muito além da faixa de 6-16 kHz dos dispositivos baseados em silício). O aumento da frequência resulta em um incremento mínimo na perda de potência, reduzindo efetivamente a ondulação da corrente e do torque do motor, ao mesmo tempo que aumenta a precisão do controle. Alta densidade de potência: Permite que componentes passivos menores (indutores e capacitores) alcancem uma corrente de saída mais alta sob as mesmas condições, suportando cargas maiores. Ambientes adversos e resposta rápida: Apresenta baixa elevação de temperatura, resistência térmica superior, resposta dinâmica rápida e adaptabilidade a condições operacionais complexas. Comparação dos parâmetros principais de drivers de motor baseados em GaN e Si (IGBT/MOSFET) - Razão de contraste: Driver de motor baseado em GaN; Driver de motor baseado em Si (IGBT/MOSFET). I. Características básicas dos materiais: gap de energia: 3,4 eV (banda proibida larga, resistente a altas temperaturas e pressões); 1,12 eV (banda proibida estreita, limite de baixa tolerância); condutividade térmica: Aproximadamente três vezes maior que a do silício (alta condutividade térmica); Valor de referência (aproximadamente 150 W/(m·K), com baixa condutividade); velocidade de saturação de elétrons: 2,8 × 10⁷ cm/s (suporta comutação de alta frequência); Aproximadamente 1 × 10^7 cm/s (desempenho limitado em alta frequência). II. Desempenho do interruptor Frequência máxima de comutação Suporta nível de MHz (tipicamente 100kHz+; alguns cenários atingem MHz) Classificado em 20kHz, mas normalmente opera entre 6-16kHz (a operação em alta frequência causa perda de potência significativa) Carga de recuperação reversa Zero (sem perda de recuperação reversa, suporta comutação de alta di/dt/dv/dt) O IGBT requer diodos em paralelo, que ainda incorrem em perda de recuperação reversa; o diodo de corpo do MOSFET tem um Qrr alto. Tempo morto Mínimo 14ns (reduz harmônicos de torque e vibração) 100-500ns (pode causar descontinuidade de corrente, levando a harmônico de torque de sexta ordem) III. Características de Perda Redução da perda de comutação (comparada ao silício) Regime discreto reduzido em 39% (11,6 W vs 19 W), regime combinado reduzido em 24,5% (12,3 W vs 16,3 W) Valor base (alta frequência causa alta taxa de perda, limitando a eficiência) aumento de frequência incremento de perda O aumento de potência é de apenas 0,7 W quando a frequência é aumentada de 20 kHz para 40 kHz, com o incremento de perda reduzido em 83%. A potência de saída aumenta em 4,1 W quando a potência de saída é aumentada de 20 kW para 40 kW (com a perda aumentando significativamente à medida que a frequência aumenta). Resistência de condução (RDS(on)) Baseada em gás de elétrons bidimensional (2DEG), é muito menor do que a de dispositivos de silício com as mesmas especificações. A resistência de condução (RDS) do MOSFET aumenta com a corrente e a temperatura, enquanto o IGBT mantém uma tensão de saturação constante, mas apresenta perda de corrente na cauda. IV. Propriedades Térmicas Resistência térmica do dispositivo (Rth (is)) Tão baixa quanto 0,5 K/W (flip-chip/CCP, caminho térmico curto) 1,5-2 K/W (encapsulamento tradicional com baixa eficiência de dissipação de calor) Diferenças na temperatura de junção com o mesmo consumo de energia Baixa temperatura do corpo (20-40 °C) (condução de calor rápida, acúmulo mínimo de calor) A temperatura é muito alta e pode acionar a proteção contra superaquecimento Necessidade de dissipadores de calor Não é necessário dissipador de calor para dispositivos abaixo de 200 W; a solução de encapsulamento selado de 1 kW elimina a necessidade de um dissipador de calor quando a corrente é inferior a 18 A. Sistemas de média e baixa potência ainda requerem dissipadores de calor, enquanto módulos de resfriamento a ar frio/líquido de grande escala para alta potência. V. Características do Projeto do Sistema Volume de componentes passivos A substituição do capacitor eletrolítico de 330 μF por um capacitor cerâmico de 22 μF reduz o tamanho do indutor (diminuindo os requisitos capacitivos-indutivos em altas frequências). Dependem de capacitores eletrolíticos e indutores de grande volume (exigindo simulação de ondulação de corrente em baixa frequência). Densidade de potência (corrente de saída) A solução discreta oferece uma relação de valor de corrente efetiva 3,5 A maior (Si), suportando maior capacidade de carga com a mesma elevação de temperatura. Valor de referência (aumento de corrente limitado por perda de potência e dissipação de calor). Interferência eletromagnética Alta integração (por exemplo, meia ponte selada), permitindo a incorporação interna do motor para reduzir o comprimento do cabo e minimizar a EMI. Layout discreto, cabo longo, forte radiação EMI em alta frequência VI. CONFIABILIDADE Tolerância à temperatura A tolerância à temperatura é muito superior à de dispositivos baseados em silício (estabilizando a operação sob alta carga). Baixa tolerância à temperatura, vida útil reduzida em altas temperaturas. Vida útil do dispositivo (modelo de Arrhenius) A vida útil dobra a cada queda de 10 °C na temperatura da junção (temperatura de junção mais baixa prolonga a vida útil). Alta temperatura do corpo e vida útil relativamente curta. Tempo Médio Entre Falhas (MTBF) Maior (baixa perda + baixo estresse térmico, reduzindo o risco de falha). Menor (maior estresse térmico e probabilidade de falha devido ao desgaste). Fabricantes e soluções típicas de GaN TI DRV7308 Pré-driver FET GaN integrado com modulação trifásica e capacidade de controle orientado a campo. Pacote QFN de 12 mm × 12 mm, com eficiência superior a 991111111111 em aplicações de acionamento de motor de 250 W, eliminando a necessidade de um dissipador de calor. Solução de baixa tensão da Innosense (entrada de 48V-60V, compatível com motores de 1kW): Esquema discreto (INNDMD48V25A1): 6 INN100EA035A + 3 INS2003FQ, com perda total de 11,6W (19W no esquema de silício) a 40kHz/20A, e aumento de temperatura de apenas 10°C quando a frequência é elevada para 40kHz. Esquema encapsulado (INNDMD48V22A1): 3 encapsulamentos de GaN em meia ponte ISG3204LA, com perda total de 12,3W (16,3W no esquema de silício) a 40kHz/20A, sem necessidade de dissipador de calor abaixo de 18A. Empresas como Texas Instruments (TI), Infineon, Innosense, EPC e Nanoware estão desenvolvendo ativamente aplicações de nitreto de gálio (GaN) em robôs humanoides, particularmente para sistemas de acionamento de motores.