The electric drive system is developing towards the multi-objective direction of compact size, low weight, high efficiency and low noise, which provides more space, higher endurance and more comfortable riding environment for the vehicle.
▶ Development Direction: Coaxial planetary gear technology aligns with the development objectives of electric drive systems and is emerging as the mainstream trend for future electric drive systems, particularly in high-torque electric drive products. To deliver high-performance experiences for users, planetary gears will gradually dominate the market. Both domestic OEMs and Tier1 manufacturers are actively investing in and developing this technology. Core components and processes of planetary gears, such as gear rings, planetary gear mechanisms, planetary carrier stamping, and welding, show significant growth potential.
To meet users’ demands for optimal handling and versatile power output across various scenarios, distributed electric drive systems (including central integrated distributed drive, wheel-side drive, and hub motors) along with multi-speed transmission systems are being deployed in specialized applications, significantly enhancing the user experience across diverse operating conditions and environments. Meanwhile, most small-torque electric drive systems continue to utilize parallel shaft transmission configurations, ensuring optimal cost-performance ratios for end-users.
▶ Supply Chain and Cooperation Model: With the country’s emphasis on the new energy vehicle industry, compared to the traditional transmission industry, the initial technical threshold and industrialization investment threshold for electric drive systems are both lower, further promoting the continuous development of China’s new energy electric drive system industry. From the initial dominance of the supply chain, it has gradually evolved into a dual-track approach of supply chain plus OEM self-developed and self-manufactured systems. As market competition intensifies and the integration level of electric drive systems continues to improve, the future supply chain will be more closely integrated with OEMs,with clear division of labor, to ensure long-term market stability.
Trends and objectives for high-efficiency transmission systems
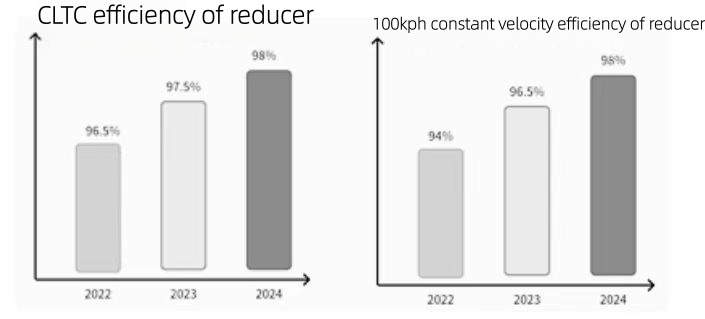
With the continuous improvement of efficiency targets, technologies such as ultra-high-precision shaft teeth, low rolling resistance bearings, low oil agitation loss shaft arrangements, active lubricant dry oil pan systems, and ultra-low viscosity lubricants will be progressively adopted. Coupled with the widespread use of coaxial planetary gear reducers, the CLTC efficiency target for transmission systems is expected to exceed 98% by 2024.
Future efficiency gains will transcend isolated upgrades to components or sub-assemblies, focusing instead on system-level optimization and integrated multi-strategy applications. Efficiency metrics will become more granular, with automakers now prioritizing real-world performance metrics like 100km/h and 120km/h steady-state range—beyond the conventional CLTC (China Light-Duty Test Cycle) benchmark—to better align with users’ daily driving needs.
Figure 3 Efficiency levels of electric drive industry reducers in the past three
ars
The trend and objectives of lightweight design
From 2027 to 2030, planetary gear sets are expected to be widely adopted in high-power, high-torque electric drive systems, reducing weight by 30% to 40% compared to current standards. With advancements in new materials (e.g., magnesium-aluminum alloy housings) and manufacturing processes (such as welding differential bolts instead of screws, and stamping die-cast differential housings), the drive system weight is projected to decrease by an additional 5%.
time
2027-2030
torque output
<3000Nm
3000-4000Nm
4000-5000Nm
Weight (dry weight)
<15kg
15-18kg
18-25kg
Table 5 Relationship between Transmission System Weight and Torque Output
Trend and goal of low-noise transmission system
To meet users’ increasingly stringent comfort requirements, the transmission system has progressively enhanced its excitation optimization and path simulation capabilities, with NVH targets varying across different vehicle classes.
Alongside advancements in simulation techniques, NVH research has shifted focus toward user-critical driving conditions. The initial development emphasis has transitioned from 100% torque NVH performance to real-world scenarios like light throttle and steady-state driving.
NVH issues are inherently systemic challenges. As user demands grow, solutions for electric drive NVH problems are evolving from isolated fixes to comprehensive system-level approaches, balancing cost-effectiveness. This includes strategies like noise masking for gear stage background noise, localized acoustic packaging, and frequency-specific optimization of acoustic materials. With continuous advancements in transmission reducer component manufacturing, noise levels in drive systems are progressively decreasing.
The noise standard of the transmission system is 1.5 m average noise, and the target trend prediction is shown in the table below.
Noise of Half-Load Bench at Full Torque Condition
time
2024-2027
2027-2030
Low-end model
70dB(A)
68dB(A)
Mid-to-high-end car models
65dB(A)
60dB(A)
Table 6: Average Noise Trends
Trends and targets of spatial dimensions
In order to meet the demand of larger interior space and platform layout of powertrain, the powertrain is required to be compact and regular in shape, and the transmission is gradually developing from parallel shaft to planetary coaxial arrangement.
The planetary arrangement offers superior spatial dimensions, particularly in the X-axis direction compared to parallel-axis configurations. With equivalent output capacity, the X-axis configuration can reduce the space requirement by approximately 40%.